Developing Secure Applications & Connected Medical Devices at Advantage
Here in the Advantage Medical Devices Lab our electronics development team and application developers are helping government, healthcare organizations and medical device developers across the globe thrive and compete (successfully) in the accelerating convergence of technologies of today’s complex and challenging medtech market. Faced with policy changes and other pressures that are driving their industry, medical device companies are on the leading edge of “the ‘big data’ revolution” in healthcare. As Information Technology capabilities advance and the infrastructures they need improve, medical devices enhanced by their link to “big data” will drive efficiencies in medical care and costs via aggregating of their information. We can help you develop today for what is coming tomorrow.
mHealth - Six Challenges & Opportunities for Healthcare Device Development
The use of health devices in consumers lives, whether mHealth (mobile Health) or Fitness is escalating in numerous arenas, but specifically at the point-of-care, in hospitals, clinics and labs as well as the home. Here are six trends that bring forth challenges and opportunities for the health & medical device industry for 2015 and 2016.

- Interoperability
It is all about the medical devices connecting to digital health applications creating an interoperable platform. Developers are providing an ecosystem of seamless population health management to hospitals, clinics and pharmaceutical companies through in-home or wearable medical devices and mHealth mobile applications.
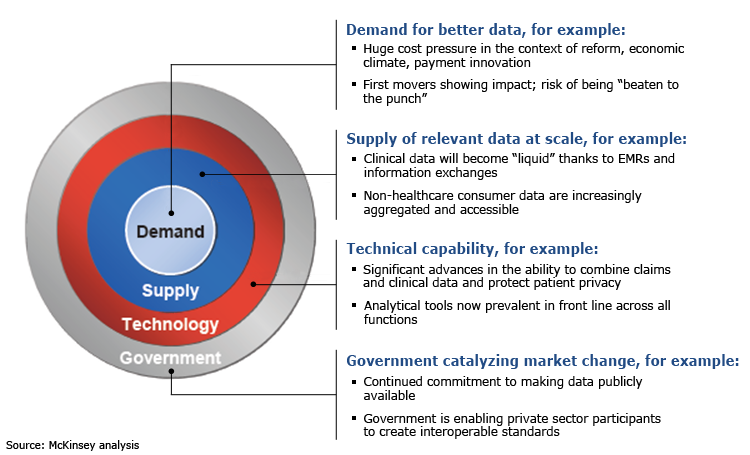
Connect to the new mobile web page content Healthcare market researcher Frost & Sullivan’s recent whitepaper explores the “intellectual vision required to look beyond the current linear process for achieving a fully integrated, real-time, health-related financial and clinical information platform and explore the endless potential for reaching this goal.”
Savings exceeding $30 billion annually is expected from increases in interoperability with its ability to share information and Electronic Health Records across medical devices, emphasis is on enhancing the value, reducing errors and streamlining workflow.
- Frugal Innovation
In an era of nearly global austerity, necessity – the “mother of invention” has brought disruptive solutions to healthcare. Imminent models, remarkably combine streamlined development practices, lean manufacturing principals; low-cost high-quality methods and combines this with social networks, most frequently utilizing mobile phones as their primary platform. Instead making existing systems “better” (read less accessible and costly), Frugal Innovation introduces more accessible, affordable and convenient solutions like the smartphone-enabled ultrasound probe that can be used for imaging organs and soft tissue or performing fetal ultrasounds anywhere.
With a reimbursement environment that is currently slow on the uptake, funding of medical device development has recently been inhibited due to investors having second thoughts about capitalizing new devices. A major dynamic motivating that trend is the rise of emerging markets where Frugal Innovation is a necessity. Adapting to meet rapidly changing market conditions means agile companies have considerable competitive advantage over many of their mature market competitors. The pressure to keep development costs down has never been more intense and although the flow of capital to early device development projects will soon begin to flow, Frugal Innovation has come to the medical device development industry to stay.
- 3D Printing has come into its own!
In 2015 to infinity it will play an ever-expanding role in the medical-device space. 3D printing has been most effective for dental work and prosthetics which can be made from flexible materials and tailored to the application. Philosophically, inventors have figured out how to how to print skin, stem cells, blood vessels and even cartilages. Strong, flexible new knee joints printed of nylon simulate bone and cartilage. New players will enter the markets with completely customizable alternative to today’s approaches and challenge conventional regulations. The FDA recognizes that evaluation of 3D-printed medical devices will require different rationale on the agencies part and is gearing up for the challenge.
- Patient Empowerment
Patients will be empowered to be more involved in their health care choices and treatment at an unprecedented level. From interactive applications on their phones to disposable patches that permit them to monitor vital information such as glucose, blood pressure hydration, highly integrated low power system on a chip (SoC) hardware now makes it possible to send data securely and interact with healthcare centers so the long excluded piece of the healthcare puzzle, patient engagement will change. With the ability to utilize these systems patients will contribute much more to their own successful health care outcomes. The patient is the key to meaningful progress in building health care systems that are effective and reliable. Their input and feedback should be welcomed and every effort fortified because ultimately the patient has more control of the outcome than the care givers do.
- Multi Functionality
Healthcare providers commonly face some of the most intricate workflow requirements there are. From communication with external providers such as insurance companies and pharmacies to managing HIPAA health information safeguards to the coordination of electronic records within departments and facilities. Increasingly, clinics and hospitals are putting a premium on training in interfaces that leverage existing knowledge. One way to do that is with multifunctional equipment a path many pioneering companies are taking.
Medical Devices that are specialized are losing ground to multi-functional, multi-parameter devices. Medical equipment that can, for example, integrate a wide variety of functions and that have connectivity, greatly expand capabilities. Increasing healthcare expenses and a growing number of systems and devices taking up floor space and care-giver’s mind share are motivating a trend particularly towards the use of networked patient monitors using Bluetooth, low energy-Bluetooth (BLE or BLE Smart), Wi-Fi and other protocols such as ANT+ that are integrated, flexible and configurable as well as secure. The evolution of personal mobile communication devices used in collaboration with these multifunctional devices greatly increase productivity and improve efficiencies across primary, secondary, and in-home care.
- New European Medical Device Regulations
Up until about 4 years ago a significant percentage of high risk class III and class IIb devices were sold without any clinical studies, but all of that is about to change. And, that is not all. FDA Notified Bodies will not only be challenging the clinical evidence for class III and IIb, but also lower risk class IIa devices and even class I devices that have been CE marked since the beginning of the Directives. Confronted with new regulations and privacy concerns the pressure for medical device development will be twitchy until the extent of increased regulation in the EU by Notified Bodies becomes clear. As the industry continues to address these ever-changing factors, developers will watch nervously as the EU decides the extent of post-Notified-Body review of high-risk devices.
